
For example, respondents may fill fields incorrectly or skip them accidentally. Typically, large data sets include errors. After this, the researcher can reach out to them through email or phone and check their responses to a certain set of questions.Ĭheck out 18 data validations that will prevent bad data from slipping into your data set in the first place. The researcher can pick a sample of 20 random respondents from each city. (Note that this can be time-consuming for surveys with lots of responses.) For example, imagine a survey with 200 respondents split into 2 cities. To do this, researchers would need to pick a random sample of completed surveys and validate the collected data.
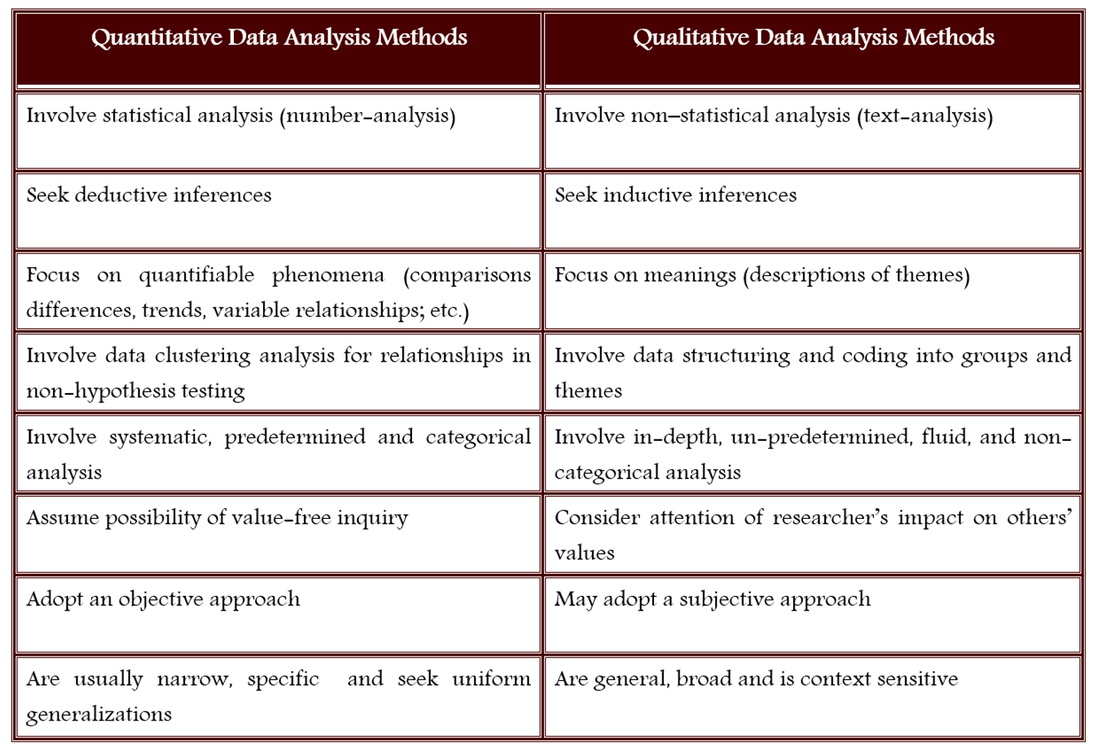

The first stage of analyzing data is data preparation, where the aim is to convert raw data into something meaningful and readable. Make sure you’re collecting high-quality data with our blog “4 Data Collection Techniques: Which One’s Right for You?”.Īnalyzing Quantitative Data Data Preparation Here are a few methods you can use to analyze quantitative and qualitative data. There are many different data analysis methods, depending on the type of research.
After collecting this information, the brand will analyze that data to identify patterns - for example, it may discover that most young women would like to see more variety of jeans.ĭata analysis is how researchers go from a mass of data to meaningful insights. For example, if a clothing brand is trying to identify the latest trends among young women, the brand will first reach out to young women and ask them questions relevant to the research objective. Similarly, in research, once data is collected, the next step is to get insights from it. We look at the data to find meaning in it. What is the first thing that comes to mind when we see data? The first instinct is to find patterns, connections, and relationships.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
